 Today I am presenting a paper from an old friend of mine. Well, “friend” is perhaps a slight exaggeration, as I have only met him a few times, but his work has nevertheless been a great inspiration to me over the years, since we work in the same field: transport network vulnerability. In 2006 Erik Jenelius from KTH in Stockholm, Sweden, together with Tom Petersen and Lars Göran Mattson published Importance and exposure in road network vulnerability analysis, where they introduce the concepts of link importance and site exposure. In the paper they calculate several indices for link importance and site exposure for the Swedish road network, based on the increase in generalized travel cost when links are closed.
Today I am presenting a paper from an old friend of mine. Well, “friend” is perhaps a slight exaggeration, as I have only met him a few times, but his work has nevertheless been a great inspiration to me over the years, since we work in the same field: transport network vulnerability. In 2006 Erik Jenelius from KTH in Stockholm, Sweden, together with Tom Petersen and Lars Göran Mattson published Importance and exposure in road network vulnerability analysis, where they introduce the concepts of link importance and site exposure. In the paper they calculate several indices for link importance and site exposure for the Swedish road network, based on the increase in generalized travel cost when links are closed.
Erik Jenelius
Erik did his PhD at KTH, the same institution that fostered Katja Berdica and her seminal paper on An introduction to road vulnerability: what has been done, is done and should be done, the very paper that led me into this field of research. I first met Erik at the NECTAR seminar on transport vulnerability in 2006, when he was still working on his PhD. By then I had already become aware of his work, but I did not know that his paper was already slotted for publication.
Exposure and importance
When it comes to measuring road network vulnerability, increased travel cost seems to be the universal measure in most papers that I have come across. Perhaps because, after all, it is the most visible and easily felt consequence of a disruption. Jenelius et al. do not simply calculate the travel cost, they link it to what they exposure and importance. In the paper they argue that
The concept of vulnerability can be divided into two parts, one containing the probability of a hazardous event and the other, which they call exposure, containing the consequences of the event in a certain place. Exposure is thus site-dependent. Similarly, we call the consequences for a collection of sites of a failing link or group of links the importance of that link or group of links. As a measure of the consequences of failure we use the increase in generalised travel cost.
In other words, vulnerability is a product of exposure and importance.
Importance versus exposure
The importance of a link refers to the increase in travel cost for the link itself, a set of links including said link, or the network as a whole. The exposure refers to the increase in travel cost for a given location, related to the expected travel demand. That means that a link may be very important in terms of increased travel cost if disrupted, but if there is little demand that would be affected by a disruption, then this location (e.g. a community) has very little exposure. Conversely, a maybe not so important link may lead to a high exposure, if travel demand is high enough.
Case study
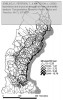
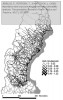
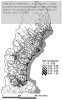
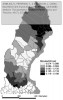
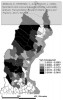
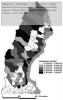
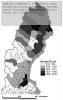
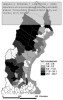
After defining several formulas, which I will not reiterate here, the authors apply their theory on the road network of Northern Sweden, where they calculate a number of measures and visualize them using GIS:
- Global link importance for the whole network
- Demand-weighted link importance for the whole network
- Unsatisfied demand-related link importance for the whole network
- Global municipality exposure to the closure of a randomly chosen link
- Demand-weighted municipality exposure to the closure of a randomly chosen link
- Unsatisfied demand-related municipality exposure to the closure of a randomly chosen link
- Global municipality exposure to the closure of the most important link
- Demand-weighted municipality exposure to the closure of the most important link
- Unsatisfied demand-related municipality exposure to the closure of the most important link
as seen in the figures below:
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
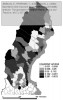 |
The figures speak for themselves, so I will not draw any conclusions here, which isn’t the point either. I only included the pictures to show how different measures yield different results, and that further analysis is necessary. The key point is that these measures can be used as a planning tool, to assess which parts of the road network that are most important, and which locations or communities that are most exposed, in case of a network disruption.
Critique
This is one of the best attempts at estimating and visualizing the social cost of road network vulnerability I have seen, and it is well worth reading the article. While vulnerability, or as the authors use, importance and exposure still hinge on the – in my opinion – imperfect measure of increased travel cost, adding importance and exposure and visualizing it using GIS brings a whole new dimension to the research of transport network vulnerability. That is the key take-home message from this article.
Reference
JENELIUS, E., PETERSEN, T., & MATTSSON, L. (2006). Importance and exposure in road network vulnerability analysis Transportation Research Part A: Policy and Practice, 40 (7), 537-560 DOI: 10.1016/j.tra.2005.11.003
Author links
- kth.se: Erik Jenelius
- kth.se: Tom Petersen
- kth.se: Lars Göran Mattsson
Other works by Erik Jenelius
- Jenelius, E (2010) Redundancy importance: Links as rerouting alternatives during road network disruptions. , Volume 3, 2010, Pages
- Jenelius E, Westin J, Holgren Å J (2010) Critical infrastructure protection under imperfect attacker perception. International Journal of Critical Infrastructure Protection, 3 (1), 16-26
- Jenelius E (2009) Network structure and travel patterns: explaining the geographical disparities of road network vulnerability. Journal of Transport Geography, 17 (3), 234-244
Related
- husdal.com: Transport Network Vulnerability Metrics