Business Week ran an article recently, stating that risk avoidance needs to be injected into employees’ thought processes, since “avoiding crises in the first place is obviously far better than having to endure the costly and disruptive consequences of dealing with such events.” I find that interesting. Risk Management is about so much more than just avoidance. In fact, there are three more ways that risk can be managed.
Business Week ran an article recently, stating that risk avoidance needs to be injected into employees’ thought processes, since “avoiding crises in the first place is obviously far better than having to endure the costly and disruptive consequences of dealing with such events.” I find that interesting. Risk Management is about so much more than just avoidance. In fact, there are three more ways that risk can be managed.
Risk Management Strategies
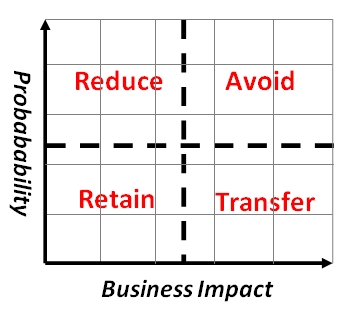
Risk reflects both the range of possible outcomes and the probabilities for each of the outcomes. A commonly used method for risk analysis is to plot unforeseen or unwanted events in a so-called risk matrix. This can be done qualitatively, where probabilities and impacts are subjective values, e.g. low/high and minor/major, or quantitatively, where probabilities and impacts are objective values, e.g. incident frequency and cost in monetary units. The simplest form of risk management then uses this matrix to discern four possible management strategies, illustrated in the figure below:
- Avoid, in case of high probability/high impact
- Transfer, in case of high probability/low impact
- Reduce, in case of low probability/high impact
- Accept or Retain, in case of low probability/low impact
Avoid-risks are risks that no business can survive in the long run, if left unattended. That is why these risks need to be avoided. Transfer-risks are not as critical as the aforementioned, but still warrant attention due to their potential disastrous impacts. Transfer means pooling or sharing risks, and insurance is one central element here. Reduce-risks often relate to day-to-day issues and operational events, and although perhaps insignificant on their own, the aggregate impact of these risks can eventually compromise operational efficiency.
Risk Ignorance
The opposite of risk avoidance is risk ignorance. More often than not businesses simply accept that they are exposed to risks and do not bother to spend much effort on assessing and mitigating these risks, regardless of which category these risks fall into. I am not sure whether I should call this to accept risk, since it is more like to willingly ignore risk, as said in the article in BusinessWeek:
Despite these high stakes, many corporations do not have a consistent or disciplined approach to risk management and accountability for product safety. That is a mistake. It is critical for businesses to consider how to reduce risk with such measures as a systematic application of “lessons learned,” or undertaking a review of the critical decision-making processes involved in producing a product.
It remains to be seen whether businesses will actually learn their lesson or not.
Links
- BusinessWeek – Creating a Culture of Risk Avoidance
Related
- husdal.com: The six ways of dealing with risk