 It is not often that I find a PhD dissertation that is excellently written and a joy to read, keeping my attention from beginning to end. The DRISC model by Ulf Paulsson is such a dissertation and it has been a great inspiration and a great reference to me. Ulf Paulsson is an Associate Professor at the Division of Engineering Logistics at Lund University, Sweden and he is the Editor of the ISCRIM Newsletter, which is how I came across the dissertation in the first place. What makes this dissertation so special?
It is not often that I find a PhD dissertation that is excellently written and a joy to read, keeping my attention from beginning to end. The DRISC model by Ulf Paulsson is such a dissertation and it has been a great inspiration and a great reference to me. Ulf Paulsson is an Associate Professor at the Division of Engineering Logistics at Lund University, Sweden and he is the Editor of the ISCRIM Newsletter, which is how I came across the dissertation in the first place. What makes this dissertation so special?
A new model
The Disruption Risks in Supply Chain (DRISC) model is developed for investigating all kinds of disruptions that can potentially occur in the supply chain flow along the way from raw material to finished product. The risks are classified and summarized into an expected consequence value.
The DRISC Model
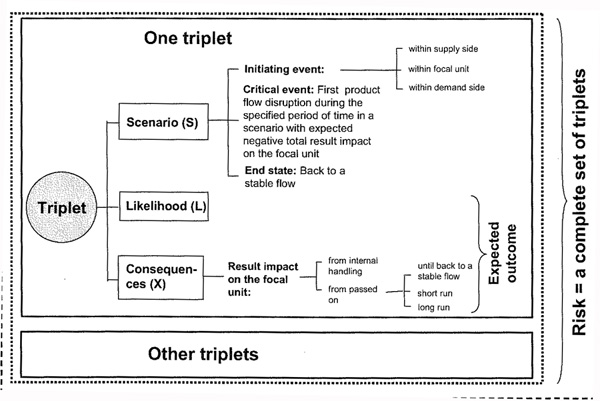 Building on Garrick and Kaplan’s risk triplet, the beauty of Paulsson’s model is that gives and overall picture of the risk exposure, the consequences and the long-term effects of supply chain disruptions. The DRISC model provides not only a framework for system description and analysis, but also a framework for the risk management process, as in risk analysis, risk evaluation and risk control.
Building on Garrick and Kaplan’s risk triplet, the beauty of Paulsson’s model is that gives and overall picture of the risk exposure, the consequences and the long-term effects of supply chain disruptions. The DRISC model provides not only a framework for system description and analysis, but also a framework for the risk management process, as in risk analysis, risk evaluation and risk control.
Kaplan’s risk definition
The definitionof risk in Kaplan and Garrick (1981) splits the concept of risk into three different elements, together called a triplet. Each triplet identifies a risk scenario, involving a source, a likelihood and an impact:
- What can happen and what is the cause?
- How likely is it that it will happen?
- If it does happen, what are the consequences?
A risk can be seen as incompletely described unless all three elements are in place. An untrained individual or business entity often stops short after the first, or maybe the second question, without fully considering the third. In risk management, addressing the impacts is an important issue, which is why the consequences need to be considered along with the likelihood and source of risk.
Risk handling strategies
Paulsson summarizes the current literature into 22 risk handling strategies and discusses how they contribute to a company’s risk exposure:
Accept Avoid, Back-up, Buffer, Concentrate Create, Diversify, Reserve, Relate, Identify, Insure, Organize, Overcapacitize, Protect, Replace, Secure, Train, Transfer, Qualitize, Quantify
Seeing is believing
![]() What strikes me most about the dissertation are the clear-cut and self-explanatory figures graphs and tables. It is evident that Paulsson knows his subject.
What strikes me most about the dissertation are the clear-cut and self-explanatory figures graphs and tables. It is evident that Paulsson knows his subject.
State of the art literature review
One of the stated objectives of the dissertation was to identify, structure and summarize the state of the art on supply chain disruption risk, and Paulsson does an excellent job at that. Seldom I have I seen a literature review that so brilliantly captures the essence of the current research strands. Much of the literature was already familiar to me, but Paulsson managed to bring it together in a readable and clear fashion that made pefect sense. In fact, I found it to be so well written that I used much of it for a guest lecture I did on supply chain risk at Molde University College. For that alone, the dissertation is worth a read.
References
Paulsson, U. (2007). On Managing Disruption Risks in the Supply Chain – the DRISC Model. Unpublished PhD, Lund University, Lund.
Paulsson, U. and Nilsson, C.-H. (2008) Potential Risk Handling Alternatives for Supply Chain Disruptions in Liquid Food Production – the case of V&S Vin & Sprit AB, the Sundsvall site. LUCRAM report 1015/2008. Lund University Centre for Risk Analysis and Management, Lund, Sweden. (How to apply the DRISC model)
Kaplan, S., & Garrick, B. (1981). On The Quantitative Definition of Risk Risk Analysis, 1 (1), 11-27 DOI: 10.1111/j.1539-6924.1981.tb01350.x
Author link
- researchgate.net: Ulf Paulsson
Download
Related
- husdal.com: Supply Chain Risk lecture