 Today’s article is one of the earlier works on supply chain vulnerability, published in 2000. A conceptual framework for the analysis of vulnerability in supply chains by Göran Svensson uses the Swedish car manufacturer Volvo as grounds for establishing his theoretical framework. This is the first of two papers on the same topic; this paper deals particularly with the inbound supply chain. A second paper, which I will review tomorrow, deals both with inbound and outbound logistics.
Today’s article is one of the earlier works on supply chain vulnerability, published in 2000. A conceptual framework for the analysis of vulnerability in supply chains by Göran Svensson uses the Swedish car manufacturer Volvo as grounds for establishing his theoretical framework. This is the first of two papers on the same topic; this paper deals particularly with the inbound supply chain. A second paper, which I will review tomorrow, deals both with inbound and outbound logistics.
Two dimensions
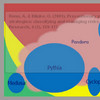
Separating the chaff from the wheat and diving straight into the essence of the paper, Svensson aligns his framework along two dimensions, categories of disturbance and sources of disturbance. He then divides the categories into either quantitative or qualitative disturbances. Sources of disturbance are either atomistic (direct) or holistic (indirect).
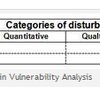
Categories of disturbance
Disturbances are either quantitative or qualitative.
Disturbances are quantitative if they lead to a lack of materials or components. Causes for such disturbances are usually a breakdown in inbound logistics, e.g. delays in inbound transport due to accidents, bad weather or any other reason for a “no-show” of components or materials.
Disturbances are qualitative if they lead to defects in components or materials. Causes are events that lead to poor paint, uneven surfaces, measurement errors or any other kind of malfunctional or non-fitting components or materials.
Sources of disturbance
The supply chain of incoming materials and components can be seen form a narrow or a wide perspective. The narrow or atomistic vulnerability perspective focuses on the immediate cause, and is applicable if the disturbance has its source and impact limited to a small part of the supply chain, i.e. immediate cause and immediate impact and immediate remedy. The wide or holistic vulnerability perspective is applicable if the disturbance has a cause outside the immediate event, i.e. in the upstream supply chain, and if the event impacts the supply chain further downstream.
The framework matrix

Svensson (2000): Framework for Supply Chain Vulnerability Analysis
Conclusion
Svensson argues that, based on his empirical findings, the two dimensions (sources and categories of disturbance) are highly valid, reliable and universally applicable, and I am am inclined to second his notion. Indeed, it is a useful and practical approach. One perspective is lacking though, and that is the outbound logistics flow.
This framework looks exclusively at the inbound flow, and although the holistic approach does acknowledge a downstream impact, this impact is not further analyzed. However, in a second paper, following up on this research, Svensson has incorporated both inbound and outbound flow, and that will be the topic for tomorrow’s post.
Reference:
Svensson, G. (2000). A conceptual framework for the analysis of vulnerability in supply chains International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 30 (9), 731-750 DOI: 10.1108/09600030010351444
Links
- Halmstad University: Göran Svensson‘s homepage
- nordinavia.se: Göran Svensson’s full professional profile and CV