Accuracy
Using raster GIS for network analysis leads into a simplification of a complex network structure. The path is prone to be distorted, firstly, due to the mistaken length introduced by Incremental Length, and secondly, due the zigzagged path, a consequence of the innate grid structure. Nonetheless, a fine-tuned use of Incremental Linkage and a minimal cell resolution can have a smoothing effect on the exact delineation of the path. On the other hand, minimising cell resolution increases computation.
In raster GIS the precision of the model is determined by the cell resolution, the finer the resolution (the smaller the cell size), the better the precision. For this research a cell resolution of 20m was deemed appropriate for the task in question, as it would allow encompassing normal road width and adjacent areas within one cell width. For a dense inner city road network a cell resolution of 10m would be preferable, allowing even narrow blocks to be incorporated into the model.
The infamous multiple path problem
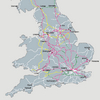
The concept of adding proximity surfaces will some times lead to peculiar artefacts. A special case appears in a regular lattice if the cost surface is isotropic: Here the multiple path problem is clearly visible, since all possible paths per se have the same accumulated cost towards the destination. Here, human mind, as opposed to computer mind, would intuitively seek out a solution that implements a heuristic search, always following the path that yields the shortest Euclidian distance to the destination.

Multiple path problem in regular lattice with homogenous cost surface. Start at top left, destination at bottom right.
More often occurs the so-called multiple path problem, particularly if the road network and the cost surface are oversimplified. There are no distinctive low values, so that in order to gain a coherent route from start to destination so many low valued cells have to be selected that no clear path can be discerned.
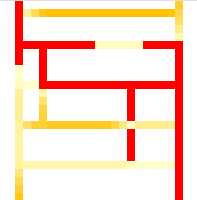
Typical multiple path problem. Start at top left, destination at bottom right.