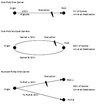
The procedure is similar to finding the shortest path through a network with no time-dependent travel cost.
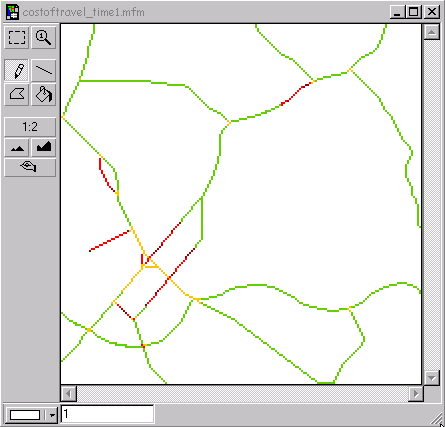
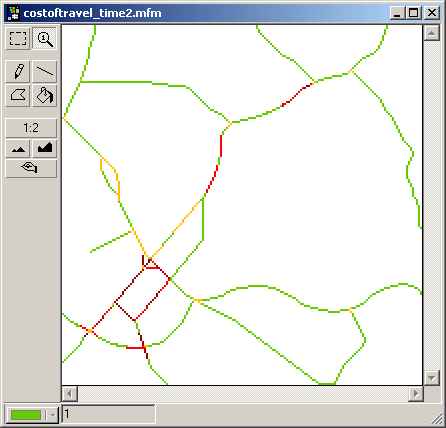
First calculate the path(s) from origin to the cutoff-point(s), where the new time interval starts. In other words spread until the available time in time interval 1, depending on your starting time, has been used up. From the cutoff-point(s) in time interval 1, calculate the shortest path(s) to the destination through time interval 2. The path with the lowest value is the sought path. Join the paths.
The cell value at the cutoff-point for time interval 1added to the cell values of the shortest path in time interval 2 is the total cost for the joined path.
If using 3 time intervals, repeat the procedure for time interval 1 in time interval 2. If using 4 time intervals, repeat the procedure for time interval 2 in time interval 3, and so forth.
See the theory behind it.
Map layers needed:
network.mfm
costoftravel_time1.mfm
costoftravel_time2.mfm
start.mfm
stop.mfm