This operation infers the lineal characteristic of raster cells, by equating consecutive locations with a set of straight lines between them (Figure 1-3). Based on its relations with neighboring cells that have the same attribute value, each cell is given a linkage value indicating how it is linked to other cells.
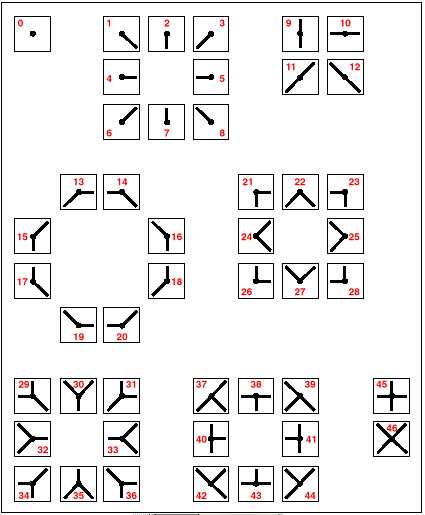
Incremental Linkage, cell value infers the linear structure it represents.
© Thinkspace
By assigning a value to each cell equivalent to the linear feature it represents it is possible to create a network similar to a road network. The smaller the cell resolution, the better the real-world road network will be approximated by this procedure.
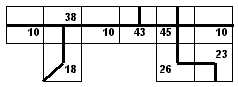
Building a road network using Incremental Linkage from
figure 1-3 with cell values representing linear features
The second step to creating a road network in raster GIS is to impose constraints on the flow that can take place from cell to cell.