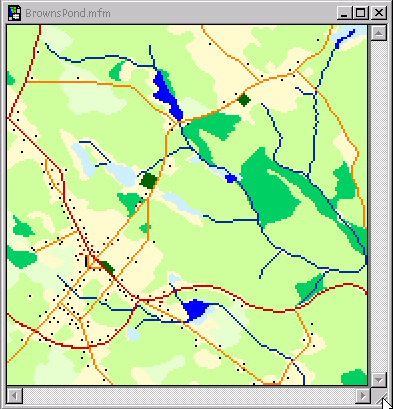
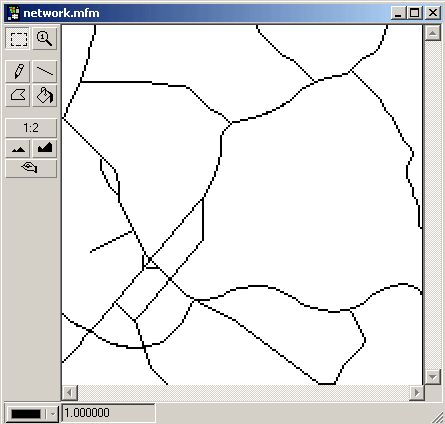
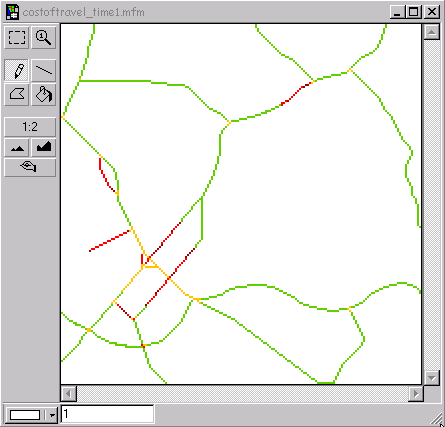
Usually, to generate a cost-of passage surface, several variables will be collapsed into one layer. These variables might be road class, average speed, traffic density, and congestion during specific time of day or other factors that contribute to the overall cost variable. The cost-of-passage surface can be defined by a variety of measurement units: time, fuel consumption, money or other possible cost units, for which the least cost passage is to be determined.
Using average speed and time as a means of inferring cost-of-passage is among the most common approach in network analysis, since it is easy to use and calculate. However, “least cost” does not always need to be “least time”; it may just as well be least fuel,
…